Decision Matrix
Overview
Decision Matrix provides a visual, table-driven approach to complex business rule implementation. By mapping input values on X and Y axes to specific outcomes, Decision Matrix enables sophisticated decision logic that can be easily understood, maintained, and modified by business users without programming knowledge.
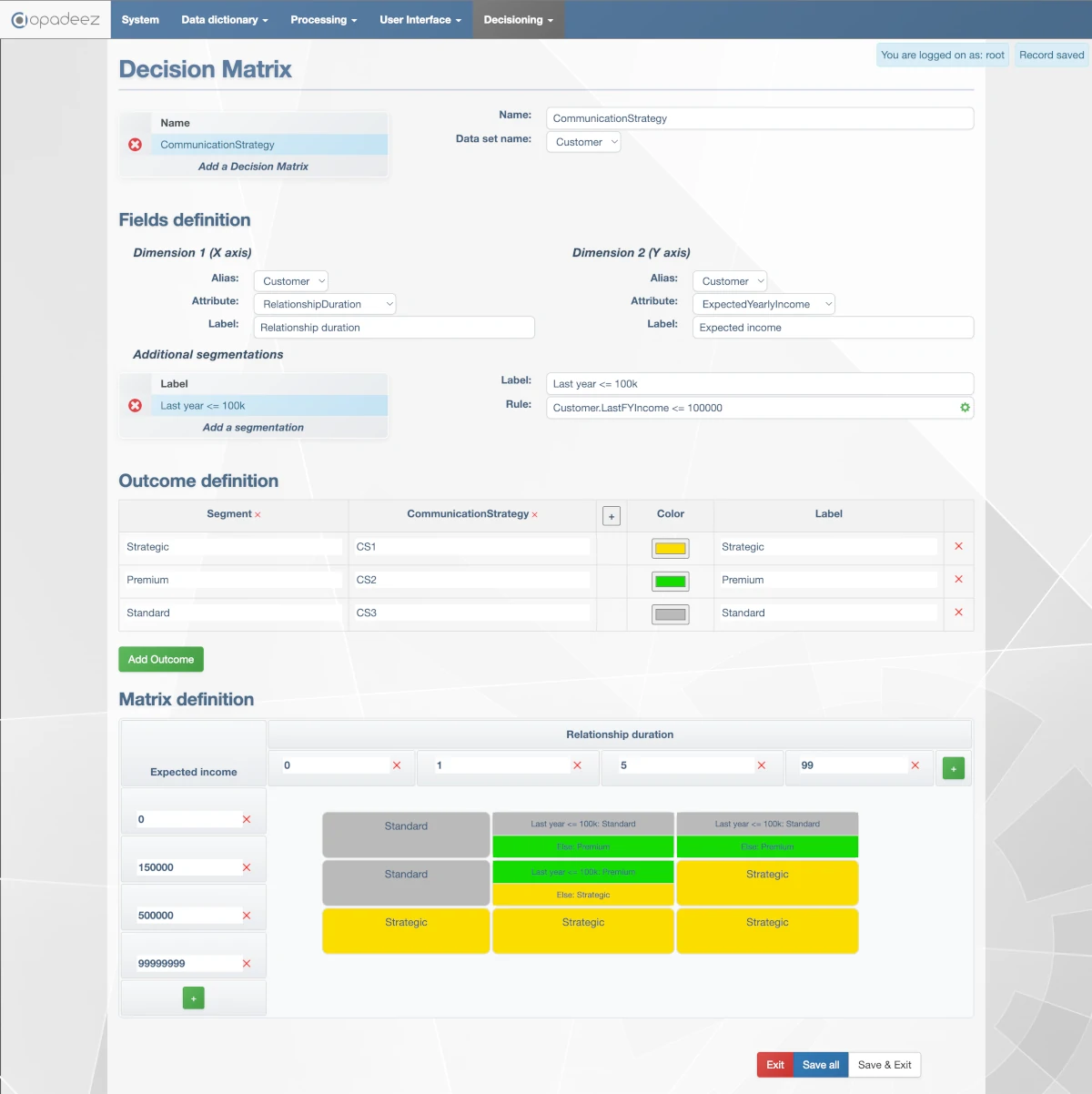
Decision Matrix interface showing communication strategy assignment using expected income and relationship duration.
What is a Decision Matrix?
A Decision Matrix is a business rule engine that:
- Maps Input Values: Uses two numeric fields as X and Y axes for decision mapping
- Defines Outcomes: Associates specific results with combinations of input values
- Supports Segmentation: Allows cell splitting for multiple outcomes within ranges (currently supports only 1 split per cell)
- Provides Visualization: Color-coded matrix for easy rule comprehension
- Enables Business Control: Non-technical users can modify decision rules
Decision Matrix Configuration
Name
- Purpose: Unique identifier for the decision matrix
- Requirement: Must be unique across all decision matrices in the system
- Usage: Referenced when calling matrix from flows using "decisionmatrix" action
- Best Practice: Use descriptive names that indicate the decision purpose
Data Set Name
- Purpose: Defines the DataSet context for matrix execution
- Data Access: Matrix can access fields from this DataSet for input values
- Integration: Links matrix to specific data structure and relationships
- Requirement: Must reference existing DataSet definition
Fields Definition
Define the numeric fields that serve as input axes for the decision matrix:
X and Y Axis Fields
Each axis requires configuration of:
Alias
- Purpose: Entity alias from the selected DataSet
- Source: Must be available in the configured DataSet
- Example: "Customer" for customer-related fields
- Context: Determines which entity provides the field value
Attribute
- Purpose: Specific numeric field from the selected alias
- Data Type: Must be numeric for proper matrix calculation
- Example: "ExpectedIncome" fields
- Range: Field values determine matrix positioning
Label
- Purpose: Display text shown in the matrix interface
- User Interface: Appears as axis labels in the visual matrix
- Clarity: Should clearly indicate what the axis represents
- Example: "Credit Score" or "Annual Income ($)"
Additional Segmentations
Enable cell splitting for multiple outcomes within the same value ranges:
Label
- Purpose: Display name for the segmentation rule
- Interface: Shown in matrix to identify the segmentation
- Clarity: Should describe the segmentation criteria
- Example: "First Time Customer" or "High Value Client"
Rule
- Purpose: Logic that determines when segmentation applies
- Script Helper: Use gear icon to access scripting assistance
- Boolean Logic: Rule must evaluate to true/false
- Scripting Language: Uses Opadeez Scripting Language syntax
- Example:
Customer.LastFYIncome <= 100000
Outcome Definition
Define the possible results that the matrix can produce:
Outcome Fields
- Add Columns: Click + to add outcome field columns
- Field Types: Can include various data types for comprehensive outcomes
- Multiple Fields: Each outcome can set values for multiple fields
- Flexibility: Supports complex outcome structures
Outcome Configuration
For each outcome, configure:
Field Values
- Purpose: Specific values assigned to each outcome field
- Data Types: Values must match field data types
- Business Logic: Represents the decision result
- Example: Segment = "Premium"
Color
- Purpose: Visual representation in the matrix
- User Interface: Cells display in selected color
- Pattern Recognition: Helps users quickly identify outcome patterns
Label
- Purpose: Text displayed in matrix cells
- Clarity: Should clearly indicate the outcome
- Brevity: Keep short for matrix readability
- Example: "Premium"
Outcome Management
- Add Outcome: Click "Add Outcome" to create new result options
- Reordering: Drag-drop lines to change outcome order
- Organization: Logical ordering improves matrix readability
- Maintenance: Easy modification of outcome definitions
Matrix Definition
Configure the actual decision grid by defining value ranges and cell outcomes:
Axis Segments
- Add Segments: Click + on X and Y axes to add value segments
- Value Entry: Key in the threshold value for each segment
- Automatic Ordering: Values are automatically sorted
- Range Creation: Segments create value ranges for decision mapping
Cell Configuration
- Cell Selection: Click on matrix cells to configure outcomes
- Outcome Assignment: Select which outcome applies to each cell
- Sub-segmentation: Create additional splits within cells if needed
- Visual Feedback: Cells display in outcome colors for immediate feedback
Practical Example: Customer Communication Strategy
Based on the interface shown:
Matrix Configuration
- Name: CustomerStrategy
- DataSet: Customer
- X-Axis: Customer.RelationshipDuration
- Y-Axis: Customer.ExpectedYearlyIncome
Segmentation Example
- Label: "Last year <= 100k"
- Rule:
Customer.LastFYIncome <= 100000 - Effect: Cells split to handle customers with high income the previous year
Outcome Examples
- Strategic: Gold color, customers with highest value
- Premium: Green color, customers with high value or long history
- Standard: Grey color, standard customers
Matrix Segments
Expected income segmented with following values:- 0 - 150,000
- 150,000 - 500,000
- > 500,000
- <= 1
- 1 - 5
- > 5
Integration with Flows
Decision Matrix Action
- Flow Integration: Use "decisionmatrix" standard action
- Action Name: References the decision matrix name
- Execution: Matrix evaluates current DataSet values
- Result Storage: Outcome values written to DataSet fields
Execution Process
- Value Retrieval: Matrix reads X and Y axis values from current record
- Segmentation Check: Evaluates additional segmentation rules
- Cell Determination: Identifies appropriate matrix cell
- Outcome Application: Applies outcome values to DataSet fields
Best Practices
Matrix Design
- Logical Axes: Choose axes that naturally correlate with decision factors
- Appropriate Granularity: Balance detail with usability
- Clear Outcomes: Define distinct, meaningful outcomes
- Color Consistency: Use intuitive color schemes
Segmentation Strategy
- Meaningful Splits: Only add segmentation when business logic requires it
- Simple Rules: Keep segmentation rules easy to understand
- Performance: Minimize complex segmentation for better performance
- Maintenance: Document segmentation logic for future updates
Business User Enablement
- Training: Provide training on matrix modification
- Documentation: Document business rules and rationale
- Testing: Establish testing procedures for rule changes
- Version Control: Track matrix changes and versions
Common Use Cases
Risk Assessment
- Credit Risk: Income vs. Credit Score
- Insurance Risk: Age vs. Driving Record
- Investment Risk: Portfolio Value vs. Risk Tolerance
Pricing Decisions
- Product Pricing: Volume vs. Customer Tier
- Service Rates: Complexity vs. Urgency
- Discount Levels: Purchase Amount vs. Customer Loyalty
Resource Allocation
- Support Priority: Issue Severity vs. Customer Tier
- Project Resources: Project Size vs. Strategic Importance
- Approval Workflows: Amount vs. Requester Level
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Missing Outcomes: Ensure all matrix cells have assigned outcomes
- Segmentation Errors: Verify segmentation rule syntax
- Data Type Mismatches: Confirm axis fields are numeric
- Performance Issues: Optimize complex segmentation rules
Testing Strategies
- Boundary Testing: Test values at segment boundaries
- Segmentation Testing: Verify segmentation rules trigger correctly
- Outcome Validation: Confirm outcomes produce expected results
- Edge Cases: Test with null or extreme values
Getting Started
Ready to create decision matrices? Follow these resources:
- Data Set Definition: Understand DataSet structure for matrix integration
- Flows: Learn how to use decision matrix actions
- Opadeez Scripting Language: Complete reference for writing segmentation rules
- Scripts: Creating standalone script actions
Related Topics
- Standard Actions: Using decisionmatrix action in flows
- Entities & Attributes: Configuring numeric fields for matrix axes
- Opadeez Scripting Language: Writing rules and segmentation logic
- Basic Concepts: Understanding Opadeez fundamentals