Decision Tree
Overview
Decision Tree provides a hierarchical, rule-based approach to complex business decision making. By creating branching logic structures that evaluate conditions sequentially, Decision Trees enable sophisticated decision processes that can be easily understood, maintained, and modified by business users without programming knowledge.
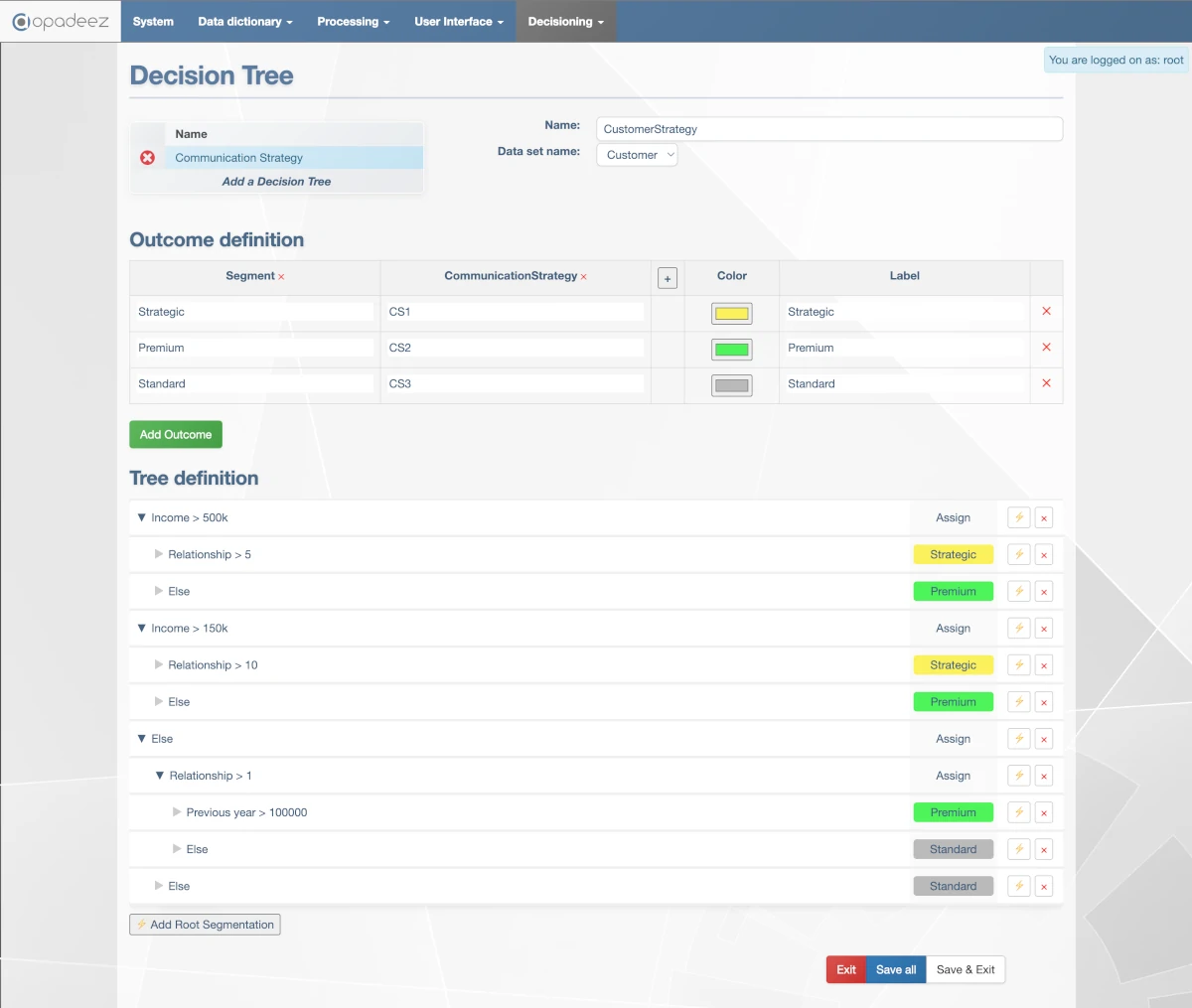
Decision Tree interface showing hierarchical customer segmentation with branching rules and outcome assignments
What is a Decision Tree?
A Decision Tree is a business rule engine that:
- Creates Hierarchical Logic: Uses branching structures to evaluate conditions sequentially
- Supports Complex Rules: Handles multiple conditions and nested decision points
- Provides Clear Flow: Visual representation of decision logic from root to outcomes
- Enables Flexibility: Easy modification of rules and addition of new branches
- Supports Business Control: Non-technical users can modify decision logic
Decision Tree Configuration
Name
- Purpose: Unique identifier for the decision tree
- Requirement: Must be unique across all decision trees in the system
- Usage: Referenced when calling tree from flows using "decisiontree" action
- Best Practice: Use descriptive names that indicate the decision purpose
Data Set Name
- Purpose: Defines the DataSet context for tree execution
- Data Access: Tree can access fields from this DataSet for rule evaluation
- Integration: Links tree to specific data structure and relationships
- Requirement: Must reference existing DataSet definition
Outcome Definition
Define the possible results that the matrix can produce:
Outcome Fields
- Add Columns: Click + to add outcome field columns
- Field Types: Can include various data types for comprehensive outcomes
- Multiple Fields: Each outcome can set values for multiple fields
- Flexibility: Supports complex outcome structures
Outcome Configuration
For each outcome, configure:
Field Values
- Purpose: Specific values assigned to each outcome field
- Data Types: Values must match field data types
- Business Logic: Represents the decision result
- Example: Segment = "Premium"
Color
- Purpose: Visual representation in the matrix
- User Interface: Cells display in selected color
- Pattern Recognition: Helps users quickly identify outcome patterns
Label
- Purpose: Text displayed in matrix cells
- Clarity: Should clearly indicate the outcome
- Brevity: Keep short for matrix readability
- Example: "Premium"
Outcome Management
- Add Outcome: Click "Add Outcome" to create new result options
- Reordering: Drag-drop lines to change outcome order
- Organization: Logical ordering improves matrix readability
- Maintenance: Easy modification of outcome definitions
Tree Definition
Configure the hierarchical decision structure by defining rules and branches:
Root Segmentation
- Add Root: Click "Add Root Segmentation" to create top-level decision points
- Primary Logic: Root segments define the main decision criteria
- Foundation: All other branches stem from root segmentations
- Multiple Roots: Can have multiple root segments for different decision paths
Segmentation Configuration
For each segmentation line, configure:
Label
- Purpose: Descriptive name for the decision rule
- Clarity: Should clearly indicate what condition is being evaluated
- User Interface: Displayed in the tree structure
- Example: "High income customer"
Rule
- Purpose: Logic that determines when this branch is taken
- Script Helper: Use gear icon to access scripting assistance
- Boolean Logic: Rule must evaluate to true/false
- Scripting Language: Uses Opadeez Scripting Language syntax
- Example:
Customer.CustomerValue > 25000orCustomer.Age >= 35
Tree Management
- Edit Segmentation: Click on any line to edit Label and Rule
- Add Child: Click "Add child" icon to create sub-segments under current line
- Delete: Click X to remove a segmentation
- Reorder: Drag-drop lines to reorganize and reposition segmentations
- Assign Outcome: Click "Assign" to link outcomes to tree endpoints
Practical Example: Customer Communication Strategy
Based on the customer segmentation approach:
Tree Configuration
- Name: CustomerCommunicationStrategy
- DataSet: CustomerManagement
- Purpose: Determine optimal communication method based on customer characteristics
Tree Structure Example
- Root Segmentation: "High Value Customer"
- Rule:
Customer.CustomerValue > 25000 - True Branch: "Premium Status Check"
- Rule:
Customer.PremiumStatus = true - True: Assign "Phone Follow-up" outcome
- False: "Age Group Check"
- Rule:
Customer.Age >= 35 - True: Assign "Direct Mail Campaign" outcome
- False: Assign "Email Communication" outcome
- Rule:
- Rule:
- False Branch: "Standard Customer Processing"
- Rule:
Customer.Age < 35 - True: Assign "Email Communication" outcome
- False: Assign "Direct Mail Campaign" outcome
- Rule:
- Rule:
Outcome Examples
- Phone Follow-up: Green color, high-value premium customers
- Email Communication: Blue color, younger customers or standard value
- Direct Mail Campaign: Orange color, older customers or specific segments
Integration with Flows
Decision Tree Action
- Flow Integration: Use "decisiontree" standard action
- Action Name: References the decision tree name
- Execution: Tree evaluates current DataSet values sequentially
- Result Storage: Outcome values written to DataSet fields
Execution Process
- Root Evaluation: Tree starts at root segmentation
- Rule Processing: Evaluates rules sequentially from top to bottom
- Branch Navigation: Follows true/false paths based on rule results
- Outcome Assignment: Applies outcome values when reaching tree endpoint
Decision Tree vs Decision Matrix
When to Use Decision Tree
- Complex Logic: Multiple sequential conditions
- Hierarchical Rules: Rules that depend on previous evaluations
- Variable Paths: Different decision paths for different scenarios
- Conditional Branching: Rules that only apply under certain conditions
When to Use Decision Matrix
- Two-Dimensional: Decisions based on two primary factors
- Range-Based: Decisions based on value ranges
- Visual Mapping: Need for visual grid representation
- Simpler Logic: Straightforward mapping of inputs to outputs
Best Practices
Tree Design
- Logical Flow: Organize rules in logical sequence from general to specific
- Clear Rules: Write rules that are easy to understand and maintain
- Balanced Depth: Avoid overly deep trees that become difficult to follow
- Complete Coverage: Ensure all possible paths lead to outcomes
Rule Development
- Simple Conditions: Keep individual rules simple and focused
- Consistent Logic: Use consistent comparison operators and formats
- Performance: Consider rule evaluation performance for complex trees
- Testing: Test all branches and edge cases thoroughly
Business User Enablement
- Documentation: Document the business logic behind each rule
- Training: Provide training on tree modification and testing
- Validation: Establish validation procedures for rule changes
- Version Control: Track tree changes and maintain version history
Common Use Cases
Customer Segmentation
- Communication Strategy: Determine optimal contact methods
- Service Levels: Assign appropriate service tiers
- Marketing Campaigns: Select targeted marketing approaches
Approval Workflows
- Loan Approval: Multi-step credit evaluation process
- Purchase Authorization: Hierarchical approval requirements
- Risk Assessment: Sequential risk evaluation criteria
Process Routing
- Support Tickets: Route issues to appropriate teams
- Lead Qualification: Determine sales process paths
- Content Personalization: Select appropriate content based on user profile
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Unreachable Outcomes: Ensure all outcomes can be reached through some path
- Rule Conflicts: Verify rules don't create contradictory conditions
- Missing Branches: Check that all true/false paths are defined
- Performance Issues: Optimize complex rule evaluations
Testing Strategies
- Path Testing: Test each possible path through the tree
- Boundary Testing: Test values at rule condition boundaries
- Edge Cases: Test with null values and extreme conditions
- Rule Validation: Verify each rule evaluates correctly
Getting Started
Ready to create decision trees? Follow these resources:
- Data Set Definition: Understand DataSet structure for tree integration
- Flows: Learn how to use decision tree actions
- Opadeez Scripting Language: Complete reference for writing decision tree rules
- Scripts: Creating standalone script actions
Related Topics
- Decision Matrix: Alternative approach for two-dimensional decisions
- Standard Actions: Using decisiontree action in flows
- Opadeez Scripting Language: Writing rules and branching logic
- Basic Concepts: Understanding Opadeez fundamentals