Scripts
Overview
Scripts enable custom business logic and calculations within your Opadeez applications. They provide server-side processing capabilities using the Opadeez scripting language, allowing you to implement complex rules, data transformations, and automated processes that go beyond standard actions.
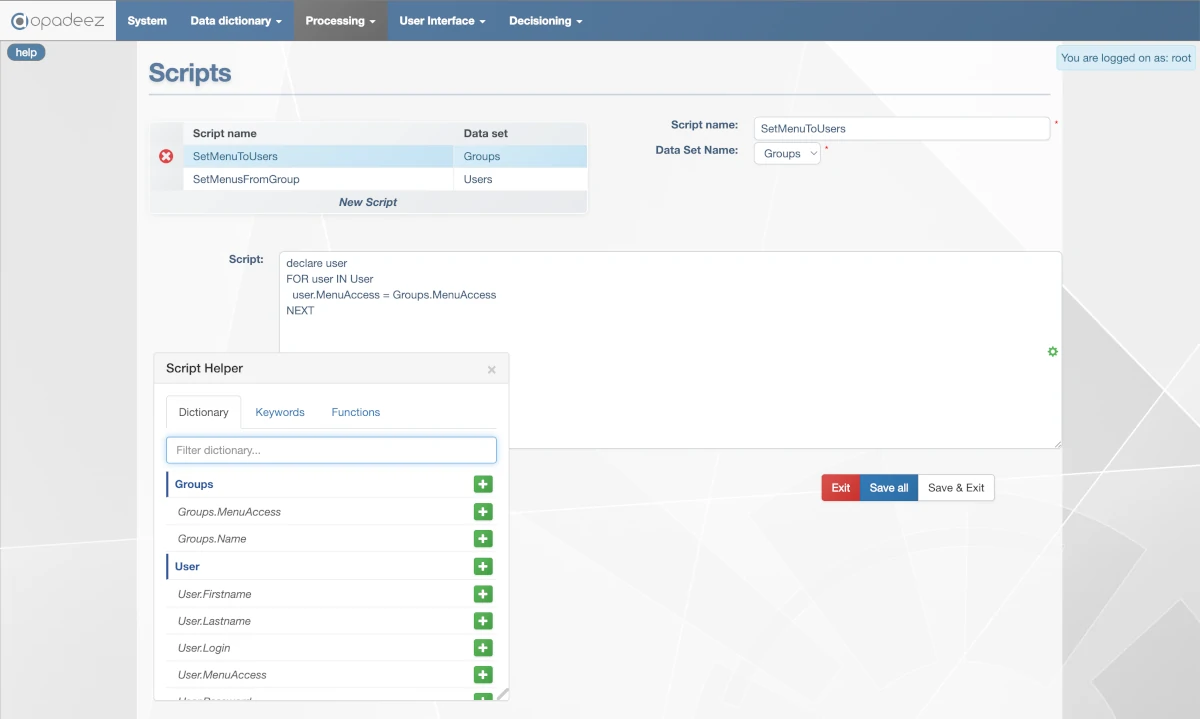
Script editor interface showing script definition, code editor, and Script Helper tools
What are Scripts?
Scripts are server-side programs that:
- Execute Business Logic: Implement custom calculations, validations, and data processing
- Process DataSet Data: Work with data from specific DataSet contexts
- Integrate with Flows: Can be called from flows using the "script" standard action
- Provide Flexibility: Handle complex scenarios that standard actions cannot address
- Support Automation: Enable automated data processing and decision making
- Use Scripting Language: Written using the Opadeez Scripting Language
Example: A script might calculate loan interest rates based on customer credit scores, update multiple related records, or integrate with external APIs for data validation.
Script Configuration
Script Name
- Purpose: Unique identifier for the script
- Requirement: Must be unique across all scripts in the system
- Usage: Referenced when calling script from flows or other components
- Best Practice: Use descriptive names that indicate the script's function
Data Set Name
- Purpose: Defines the DataSet context for script execution
- Data Access: Script processes data from this specific DataSet
- Scope Limitation: Only aliases from the selected DataSet can be used within the script
- Context Binding: Links script execution to specific data structure and relationships
Script Helper
The Script Helper (gear icon) provides development assistance with three key functionalities:
Dictionary
- Purpose: Insert alias or attribute names into the script
- Filter Functionality: Search and filter available aliases and attributes
- Accuracy: Ensures correct syntax for DataSet references
- Productivity: Reduces typing errors and speeds up development
Keywords
- Purpose: Insert keywords from the Opadeez scripting language
- Language Support: Provides access to all scripting language constructs
- Syntax Help: Ensures proper keyword usage and spelling
- Reference: Quick access to language elements without memorization
Functions
- Purpose: Insert predefined functions into the script
- Built-in Library: Access to comprehensive function library
- Parameter Guidance: Shows function signatures and parameter requirements
- Efficiency: Leverage tested, optimized functions for common operations
- Complete Reference: See Scripting Language Reference for all available functions
Script Development Process
Planning Phase
- Define Requirements: Clearly specify what the script should accomplish
- Identify DataSet: Determine which DataSet provides the necessary data context
- Map Data Flow: Understand input data, processing steps, and expected outputs
- Consider Integration: Plan how the script fits into broader workflows
Development Phase
- Use Script Helper: Leverage Dictionary, Keywords, and Functions for accurate coding
- Follow Syntax: Adhere to Opadeez scripting language conventions
- Handle Errors: Include appropriate error handling and validation
- Test Incrementally: Build and test script functionality step by step
Integration Phase
- Flow Integration: Add script actions to flows where needed
- Parameter Passing: Ensure proper data context is available
- Error Handling: Plan for script execution failures in workflows
- Performance Testing: Verify script performance under expected load
Common Script Patterns
Data Validation Pattern
- Purpose: Validate data integrity and business rules
- Process: Check field values, cross-reference data, set validation flags
- Integration: Called before save operations in flows
- Output: Set error messages or validation status fields
Calculation Pattern
- Purpose: Perform complex calculations and data transformations
- Process: Read input values, apply formulas, update calculated fields
- Use Cases: Financial calculations, scoring algorithms, aggregations
- Timing: Triggered by data changes or specific workflow steps
Data Synchronization Pattern
- Purpose: Keep related data synchronized across entities
- Process: Update dependent records when master data changes
- Scope: Work within DataSet relationships and constraints
- Consistency: Maintain data integrity across related entities
External Integration Pattern
- Purpose: Prepare data for external system integration
- Process: Format data, apply transformations, set integration flags
- Coordination: Work with External Calls for complete integration
- Error Handling: Manage integration failures and retry logic
Best Practices
Script Design
- Single Responsibility: Each script should have one clear purpose
- Modular Approach: Break complex logic into multiple focused scripts
- Clear Naming: Use descriptive names for scripts and variables
- Documentation: Include comments explaining complex logic
Performance Considerations
- Efficient Queries: Minimize database operations within scripts
- Batch Processing: Process multiple records efficiently when possible
- Resource Management: Avoid memory-intensive operations
- Execution Time: Keep scripts responsive for user-facing workflows
Error Handling
- Validation: Check input data before processing
- Graceful Failures: Handle errors without breaking workflows
- Logging: Provide meaningful error messages for debugging
- Recovery: Plan for partial failures and recovery scenarios
Maintenance
- Version Control: Track script changes and versions
- Testing: Thoroughly test scripts before deployment
- Documentation: Maintain clear documentation of script purpose and logic
- Review: Regularly review and optimize script performance
Integration with Other Components
Flow Integration
- Script Action: Use "script" standard action in flows
- Execution Context: Scripts execute within the flow's DataSet context
- Data Sharing: Scripts can modify data that flows continue to process
- Conditional Logic: Scripts can set flags for flow decision points
External Calls
- Data Preparation: Scripts prepare data for external system calls
- Response Processing: Scripts process responses from external systems
- Error Handling: Scripts manage external call failures and retries
- Data Transformation: Scripts convert between internal and external formats
User Interface
- Button Actions: Scripts can be triggered by UI button clicks
- Page Logic: Scripts can execute when pages load or change
- Field Calculations: Scripts can update calculated fields in real-time
- Validation: Scripts provide custom validation for user input
Practical Examples
Customer Credit Score Calculation
- Script Name: CalculateCreditScore
- DataSet: CustomerManagement
- Purpose: Calculate credit score based on customer financial data
- Integration: Called from customer data entry flow after save
Project Status Update
- Script Name: UpdateProjectStatus
- DataSet: ProjectManagement
- Purpose: Update project status based on task completion
- Trigger: Called when project tasks are marked complete
Data Validation Script
- Script Name: ValidateCustomerData
- DataSet: CustomerManagement
- Purpose: Validate customer information against business rules
- Usage: Called before saving customer records
Getting Started
Ready to create scripts? Follow these resources:
- Data Set Definition: Understand DataSet structure for script context
- Flows: Learn how to integrate scripts into workflows
- Standard Actions: See how to use the script action
Related Topics
- Opadeez Scripting Language: Complete syntax and function reference
- Flows: Integrating scripts into business workflows
- Lookups: Using scripts with lookup results
- Basic Concepts: Understanding Opadeez fundamentals
Pro Tip: Start with simple scripts that perform single calculations or validations, then gradually build more complex logic as you become familiar with the scripting language and Script Helper tools.