Opadeez Scripting Language
Overview
Opadeez Scripting Language has been designed to be as easy as possible to access the solution data model, implement loops and advance logic. The language provides powerful capabilities for data manipulation, calculations, and business logic implementation.
Script Helper
Where Opadeez lets user write script, there is a gear icon to open the script helper. The Script Helper provides three main categories of assistance:
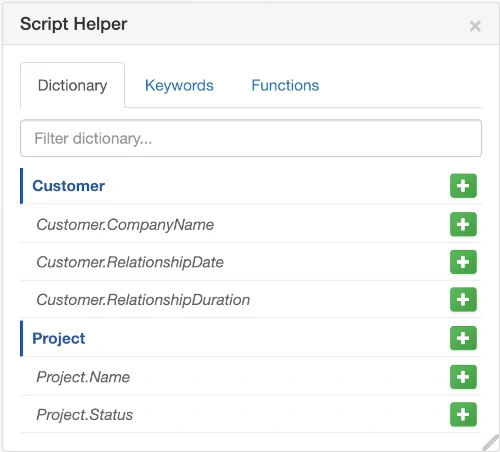
Script Helper Dictionary - Access to data model entities and attributes
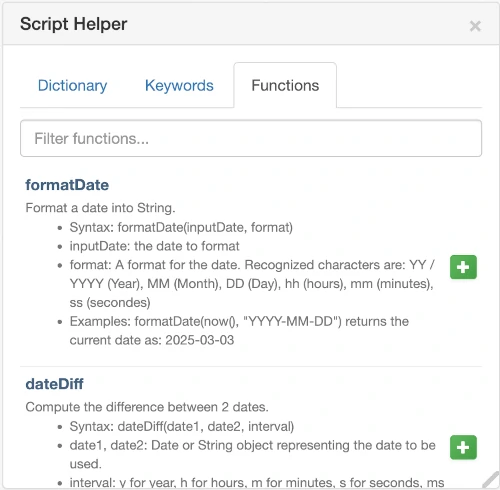
Script Helper Functions - Complete list of available functions with syntax
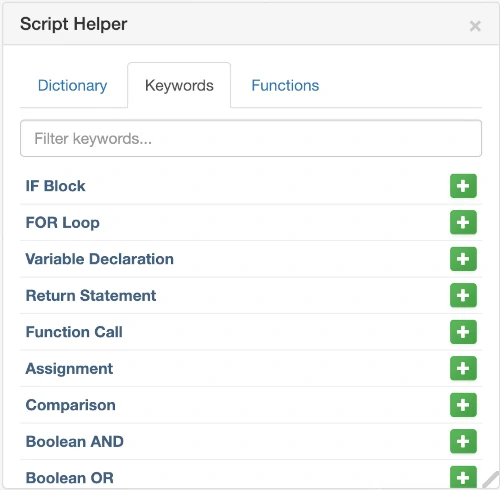
Script Helper Keywords - Language keywords and control structures
Usage Areas
Scripts can be used in different areas of a solution:
Attribute Formulas
Used to define calculated fields (Refer to Entities & Attributes for details). For Attribute formulas you should provide either:
- A single expression:
FirstName + " " + LastName - A program with a return statement:
IF LastName <> "" THEN RETURN FirstName + " " + LastName ELSE RETURN FirstName END IF
Visibility, Mandatory and Read-only Rules
Refer to Data Set Attributes Rules for details. Similarly to Attribute formulas, these rules should be either a single expression or a program with a return statement.
Scripts
Refer to Scripts for details. In this case, the script should be a Program.
Decision Matrices and Decision Trees
Used in Decision Matrix and Decision Tree for rule evaluation.
General Syntax
Expressions vs Programs
- Expressions: Single expression statement (comparison, function call, etc.)
- Programs: Multiple expressions and instructions. Use
returnkeyword if a value is expected
Instructions
- Separation: Instructions are separated by end of line character
- Example:
A = 123 B = 456 - Multi-line: Use
\character for continuation:A = 123 \ + 456
Comments
- End of line comments:
// These are comments - Multi-line comments:
/* Multi-line comments */ - Example:
// These are some comments A = 123 // These are comments /* Multi-line comments More comments*/ A = 456
Data Types and Literals
Literal Values
- Integer values:
123456 - Decimal values:
123.456 - String values:
"Some text" - Boolean values:
true,false - Null values:
null,NULL
Supported Data Types
- Number: Integer or decimal number (e.g., 123.456)
- Boolean: true or false
- String: Text values (e.g., "ABCD")
- Date: Date and time
- Alias: References to entities defined in system configuration
- Array: Array of values
Operators
Comparison Operators
==- Equal to>- Greater than>=- Greater than or equal to<- Less than<=- Less than or equal to<>- Not equal to
Boolean Operators
NOT- Logical NOTOR- Logical ORAND- Logical AND
Arithmetical Operators
+- Addition (numeric) or concatenation (mixed types)-- Subtraction/negation (numeric only)^- Power (numeric only)*- Multiplication (numeric only)/- Division (numeric only)%- Modulus
Assignment Operator
=- Assignment
Control Structures
IF Statement
IF condition THEN
program
ELSEIF condition THEN
program
ELSE
program
END IFExample:
IF A > 0 THEN
A = 123
ELSEIF B > 0 THEN
A = 789
ELSE
A = 456
END IFFOR Loop
FOR variable IN array
program
NEXTExample:
FOR account IN Customer.Account
A = A + account.Balance
NEXTVariables
Variable Declaration
Variables are created using the declare keyword:
declare A
A = 123Variable Naming
- Start with: Letter
- Followed by: Letters or digits
- Example:
myClient123is a valid variable name
Functions
Date Functions
- now(): Returns current date and time
- formatDate(inputDate, format): Format a date into String
- Format characters: YY/YYYY (Year), MM (Month), DD (Day), hh (hours), mm (minutes), ss (seconds)
- Example:
formatDate(now(), "YYYY-MM-DD")
- dateDiff(date1, date2, interval): Compute difference between dates
- Intervals: y (year), h (hours), m (minutes), s (seconds), ms (milliseconds)
- dateAdd(date, number, interval): Add intervals to a date
String Functions
- upper(inputText): Convert to uppercase
- lower(inputText): Convert to lowercase
- left(inputText, length): Returns left part of string
- right(inputText, length): Returns right part of string
- fillLeft(inputText, minimumLength, paddingCharacter): Pad string to left
- fillRight(inputText, minimumLength, paddingCharacter): Pad string to right
Numeric Functions
- roundUp(number, precision): Round up to given precision
- roundDown(number, precision): Round down to given precision
- isNumeric(value): Test if string has numeric format
Utility Functions
- iif(condition, valueIfTrue, valueIfFalse): Conditional value selection
- noNull(object, default): Return default if object is null
- randomString(length): Generate random string
- message(message, type): Display message to user (types: "I", "W", "E")
- debug(message): Output debug message to server logs
System Functions
- getProperty(propertyName): Get system property value
- getParameter(parameterName): Get context parameter value
- setLoggedUser("AliasName"): Set current logged user info
- reloadValueLists(): Reload value lists from database
- new(["AliasName"]): Create empty record for alias
- getIndex(): Get current object index in selector
- serverHook(): Run custom server hook
NULL Values
NULL values are handled gracefully in the system. Performing operations on operands having NULL values will not raise an error, however the overall expression will return null.
Example: 1 + 2 + NULL will return NULL
Data Dictionary Access
Context-Dependent Access
- Attribute formulas, visibility, mandatory, read-only rules: Attributes from the same entity can be accessed directly using their name
- Script actions: Attributes must be referenced with a specific alias name
Alias Syntax
- Basic access:
Alias.attribute - Multiple occurrences:
Alias[index]for specific element - Nested access:
Product[3].Payment[2].amount
Looping Through Multiple Occurrences
declare product, payment, sumAmount
sumAmount = 0
// Browse products
FOR product IN Product
// Browse payments for each product
FOR payment IN product.Payment
sumAmount = sumAmount + payment.amount
NEXT
NEXTData Link Attributes
Access linked entity attributes using Alias.attribute syntax. Special link attributes are automatically created for each link with the name: link<EntityFromName><LinkName>
Best Practices
Script Writing
- Use Script Helper: Leverage the gear icon for syntax assistance
- Clear Variable Names: Use descriptive names for better maintainability
- Comment Complex Logic: Document non-obvious business rules
- Handle NULL Values: Use
noNull()function for safe operations
Performance
- Minimize Loops: Avoid nested loops when possible
- Efficient Conditions: Place most likely conditions first in IF statements
- Limit Function Calls: Cache function results when used multiple times
Debugging
- Use debug() Function: Output intermediate values to logs
- Test Incrementally: Build complex scripts step by step
- Validate Data Types: Ensure operations match expected data types
Related Topics
- Entities & Attributes: Using formulas in attribute definitions
- Data Set Attributes Rules: Writing visibility, mandatory, and read-only rules
- Scripts: Creating standalone script actions
- Decision Matrix: Using scripts in decision matrix segmentation
- Decision Tree: Writing rules for decision tree branches