System Properties
Overview
System properties provide a flexible way to customize application behavior without code changes. They serve as configuration parameters that can be modified to adapt your Opadeez application to specific requirements, integrate with external systems, or control feature availability.
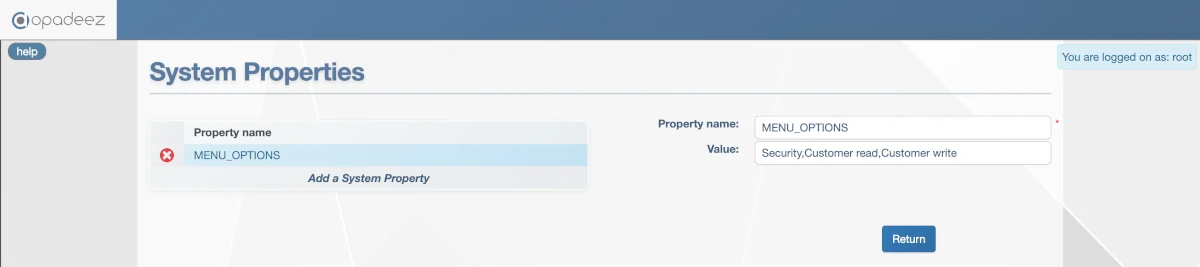
System Properties interface for customizing application behavior
Purpose and Usage
System properties provide multiple benefits for application configuration:
- Configuration: Store application-wide settings that control system behavior
- Customization: Modify functionality for specific business requirements
- Integration: Configure connections and parameters for external systems
- Feature Flags: Enable or disable functionality without code deployment
- Environment Management: Different settings for development, testing, and production
Property Configuration
Property Name
- Purpose: Unique identifier for the property
- Requirements: Must be unique within the system
- Best Practice: Use descriptive, uppercase names with underscores (e.g., API_ENDPOINT, MAX_RETRY_COUNT)
- Convention: Follow consistent naming patterns across your application
Property Value
- Purpose: The actual configuration value used by the application
- Format: Can be strings, numbers, boolean values, or complex configurations
- Usage: Referenced in scripts, flows, and other system components
- Flexibility: Can be changed without redeploying the application
Common System Properties
MENU_OPTIONS
Used by the UserManagement module to define available menu access options:
- Format: Comma-separated list of menu access options
- Example:
Security,Customer read,Customer write,Admin access - Usage: Maps to menu IDs for granular access control
- Function: Controls which menu options appear in user management interfaces
Property Usage in Scripts
Accessing Properties
System properties can be accessed in Opadeez scripts using built-in functions:
- Function: Use system property functions to retrieve values
- Function syntax: getProperty(propertyName)
- Type Conversion: Automatic conversion to appropriate data types
Security Considerations
Sensitive Information
- API Keys: Store securely, consider encryption for sensitive keys
- Passwords: Never store plain text passwords in properties
- Access Control: Limit who can view and modify system properties
- Audit Trail: Track changes to sensitive properties
Best Practices
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive property values
- Environment Variables: Use environment variables for deployment-specific secrets
- Documentation: Document the purpose and format of each property
- Validation: Validate property values before use
Property Management
Adding Properties
- Navigate: Go to System Definition → Basic Configuration
- Scroll: Find the System Properties section
- Add: Click to add new property
- Configure: Set property name and value
- Save: Save the system configuration
Modifying Properties
- Runtime Changes: Properties can be modified without redeployment
- Immediate Effect: Changes take effect immediately for new requests
- Testing: Test property changes in development first
- Backup: Document original values before changes
Best Practices
Naming Conventions
- Descriptive Names: Use clear, self-documenting property names
- Consistent Format: Follow uppercase with underscores pattern
- Grouping: Use prefixes to group related properties (e.g., EMAIL_*, API_*)
- Avoid Abbreviations: Use full words for clarity
Maintenance
- Regular Review: Periodically review and clean up unused properties
- Version Control: Track property changes in your deployment process
- Testing: Test property changes in non-production environments
- Backup: Include properties in system backup procedures
Related Topics
- Basic Configuration: Learn about overall system configuration
- Scripts: See how to use properties in custom scripts
- Flows: Understand how properties affect workflow behavior
- System Includes: Learn about sharing configurations across systems
Pro Tip: System properties are powerful tools for configuration management. Use them to avoid hardcoding values and make your applications more flexible and maintainable across different environments.