Jobs
Overview
Jobs enable automated processing by triggering flows based on specific events or schedules. They provide unattended execution capabilities for file processing, scheduled tasks, and system automation. Jobs are essential for building robust, automated business processes that run without user intervention.
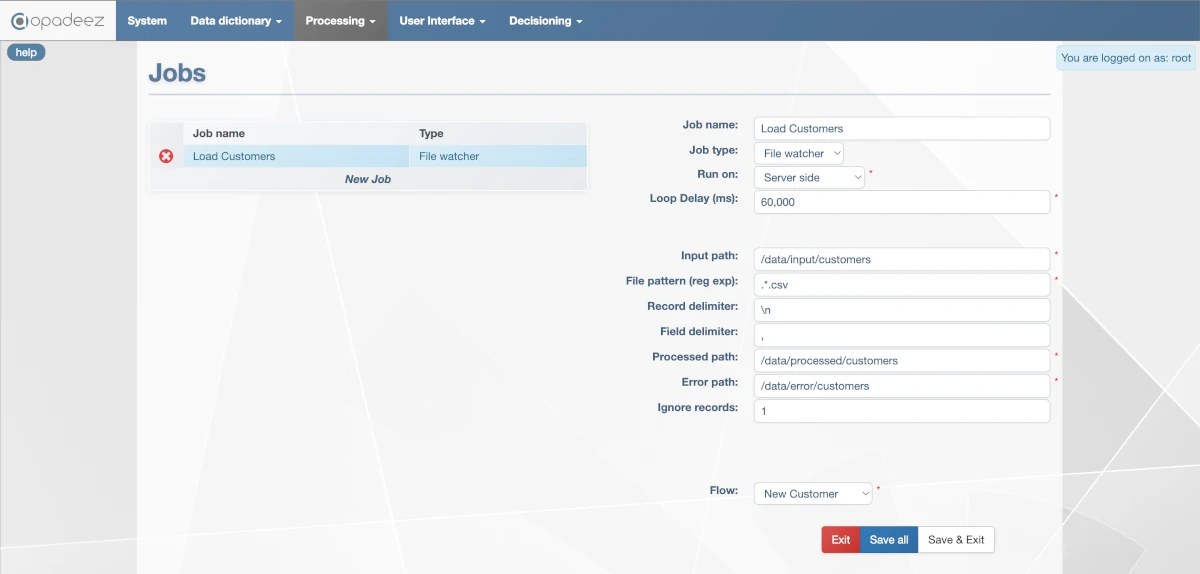
File Watcher job configuration showing input path, file patterns, and processing settings
What are Jobs?
Jobs are automated processes that:
- Trigger Automatically: Execute flows based on events or schedules without user intervention
- Process Files: Automatically handle file uploads and data imports
- Run Scheduled Tasks: Execute periodic maintenance, reports, or data synchronization
- Enable Integration: Support automated data exchange with external systems
- Provide Reliability: Handle errors and move processed files appropriately
Job Types
File Watcher
Automatically processes files when they are dropped into a specified folder. Supports CSV and hierarchical CSV formats aligned with DataSet definitions.
Hierarchical CSV Example
Customer,CUST0001,John,Doe Project,PROJ0001,Website Development,Active ProjectTask,TASK0001,Design Homepage,In Progress ProjectTask,TASK0002,Setup Database,Completed Customer,CUST0002,Jane,Smith Project,PROJ0002,Mobile App,Planning ProjectTask,TASK0003,Requirements Analysis,Not Started
In this example, the flow executes once for Customer "John Doe" with related projects and tasks, then separately for Customer "Jane Smith" with her data.
Scheduler
Triggers processes at specified intervals using cron-like scheduling. Used for periodic tasks such as checking emails, generating reports, or data synchronization.
General Job Properties
Job Name
- Purpose: Unique identifier for the job
- Requirement: Must be unique across all jobs in the system
- Usage: Referenced in monitoring and logging systems
- Best Practice: Use descriptive names indicating the job's purpose
Job Type
- File Watcher: Processes files dropped into monitored folders
- Scheduler: Executes at specified time intervals
- Configuration: Determines which specific properties are available
- Behavior: Defines how and when the job executes
Run On
Specifies execution location in 3-tier deployments where Web and Application servers are separated:
- Server Side: Job executed by the Application server
- Web Server Side: Job executed by the Web application
- Performance: Application server typically better for resource-intensive jobs
- Access: Consider file system access and network connectivity
Flow
- File Watcher: Flow executes for each group/record in the file
- Scheduler: Flow executes once per scheduled trigger
- DataSet Context: Flow must use DataSet compatible with job data structure
- Error Handling: Flow should include appropriate error handling logic
File Watcher Properties
Loop Delay (ms)
- Purpose: Frequency of checking for new files
- Example: 1,000 ms = check every second
- Performance: Balance responsiveness with system load
- Recommendation: Use longer delays for high-volume environments
Input Path
- Purpose: Folder path where input files are dropped
- Access: Must be accessible by the execution server
- Security: Ensure appropriate folder permissions
- Monitoring: Job continuously monitors this location
File Pattern (Regular Expression)
- Purpose: Defines which files to process
- CSV Files:
.*\.csvprocesses any file ending with .csv - Specific Names:
customer_.*\.txtprocesses customer files - Flexibility: Supports complex pattern matching
Record Delimiter
- Purpose: Separates records in the file
- CSV Standard:
\nfor carriage return - Windows:
\r\nfor Windows line endings - Custom: Any character sequence can be used
Field Delimiter
- Comma:
,for standard CSV files - Tab:
\tfor tab-separated values - Pipe:
|for pipe-delimited files - Custom: Any character can serve as field delimiter
Processed Path
- Purpose: Destination for successfully processed files
- File Management: Keeps input folder clean
- Audit Trail: Maintains record of processed files
- Recovery: Enables reprocessing if needed
Error Path
- Purpose: Storage location for records that caused errors
- Error Isolation: Separates problematic records for review
- Debugging: Helps identify data quality issues
- Recovery: Allows correction and reprocessing of failed records
Ignore Records
- Purpose: Number of lines to skip from file beginning
- Header Lines: Use 1 to skip CSV header row
- Multiple Headers: Use higher numbers for complex file formats
- Data Validation: Ensures only data records are processed
Scheduler Properties
Scheduler configuration follows cron table principles, defining when jobs execute based on time criteria:
Scheduling Fields
- Minutes: Specific minute of the hour (0-59)
- Hours: Specific hour of the day (0-23)
- Day of Month: Specific day of the month (1-31)
- Month: Specific month (1-12 or month names)
- Day of Week: Specific day of the week (0-7 or day names)
Scheduling Examples
Every Minute
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Minutes | <blank> |
| Hours | <blank> |
| Day of Month | <blank> |
| Month | <blank> |
| Day of Week | <blank> |
Every Hour (at minute 0)
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Minutes | 0 |
| Hours | <blank> |
| Day of Month | <blank> |
| Month | <blank> |
| Day of Week | <blank> |
Daily at 7:00 AM
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Minutes | 0 |
| Hours | 7 |
| Day of Month | <blank> |
| Month | <blank> |
| Day of Week | <blank> |
Every Sunday at 7:00 AM
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Minutes | 0 |
| Hours | 7 |
| Day of Month | <blank> |
| Month | <blank> |
| Day of Week | Sunday |
Practical Examples
Customer Data Import Job
- Job Name: CustomerDataImport
- Job Type: File Watcher
- Flow: CustomerImportFlow (uses CustomerManagement DataSet)
- Input Path: /data/import/customers/
- File Pattern: customer_.*\.csv
- Use Case: Automatically import customer data from partner systems
Daily Report Generation
- Job Name: DailyReportGenerator
- Job Type: Scheduler
- Schedule: Daily at 6:00 AM
- Flow: GenerateDailyReports
- Use Case: Generate and email daily business reports
Project Status Sync
- Job Name: ProjectStatusSync
- Job Type: Scheduler
- Schedule: Every 15 minutes
- Flow: SyncProjectStatus
- Use Case: Keep project status synchronized with external project management tools
Best Practices
File Watcher Jobs
- File Validation: Include data validation in processing flows
- Error Handling: Design flows to handle malformed data gracefully
- File Management: Ensure processed and error paths are properly configured
- Performance: Use appropriate loop delays to balance responsiveness and load
Scheduler Jobs
- Timing: Schedule jobs during low-usage periods when possible
- Dependencies: Consider dependencies between scheduled jobs
- Monitoring: Implement logging and alerting for failed scheduled jobs
- Resource Usage: Monitor system resources during scheduled job execution
General Job Management
- Naming: Use clear, descriptive job names
- Documentation: Document job purposes and dependencies
- Testing: Thoroughly test jobs in development environments
- Monitoring: Implement job execution monitoring and alerting
Integration with Other Components
Flow Integration
- DataSet Compatibility: Ensure job DataSet matches flow requirements
- Error Handling: Include appropriate error handling in job flows
- Data Validation: Validate input data before processing
- Logging: Include logging for job execution tracking
External Systems
- File Formats: Coordinate file formats with external systems
- Timing: Align job schedules with external system availability
- Error Recovery: Plan for external system failures and recovery
- Security: Implement appropriate security for file access
Troubleshooting
Common File Watcher Issues
- File Access: Verify folder permissions and network connectivity
- Pattern Matching: Test regular expressions with sample filenames
- Data Format: Ensure file format matches DataSet structure
- Processing Errors: Check error path for failed records
Common Scheduler Issues
- Schedule Configuration: Verify cron-like schedule settings
- System Time: Ensure server time zones are correctly configured
- Resource Conflicts: Check for resource conflicts with other scheduled jobs
- Flow Execution: Verify flow can execute successfully in job context
Getting Started
Ready to create jobs? Follow these resources:
- Flows: Understand flow design for job execution
- Data Set Definition: Learn DataSet structure for job data
- Your First Application - Part 4: See automation in practice
Related Topics
- Flows: Creating flows for job execution
- Scripts: Using scripts within job flows
- Basic Concepts: Understanding Opadeez fundamentals